 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
In 1955 the modulator/demodulator (modem) was invented, allowing use of audio
telephone lines for data communication. By 1956 one was permitted to
transmit non-spoken sounds over telephone lines for simple image scan
transmission. Starting in 1958, telephone company did provide what
they called a `dataset', that could be leased for about $40/month
Up to 1969 FCC regulations, instigated by the telephone companies, did not allow customers to directly connect equipment not provided by the telephone company to their lines. The court case for gaining access for connecting radio-telephones (the 1968 Carterphone Decision) had been filed by Thomas Carter of Carter Electronics of Dallas first in 1958 and refiled in 1966. It still required protective interface devices. It took to 1978 to allow direct connection to RS-11 and similar plugs and get all the new tariffs in place.
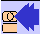
To avoid this cost and hassle Accoustic Modems or Couplers were
developed around 1966, a.o.. by John Van Geen at Stanford Research
Institute, that mimicked handset operations. One would dial the
computer system (which would have telephone company datasets) on one's
phone, and when the connection was established, place the handset into
the accoustic modem. Since the handsets were all supplied by the
telephone company, most had the same shape, simplifying the physical
Interface.
A microphone and a speaker inside the modem box would
pick up and transmit the signalling tones, and circuitry would convert
those audio shift-key encoded frequency binary
signals for an RS232 output socket. With luck one could get 300 baud
(~bits/second) transmission rates, but 150 baud was more typical. That
speed was sufficient for typewriter-based terminals, as the IBM 2741,
running at 147.5baud, or a teletype, running at 110baud.
The model shown was built by Livermore Data Systems. Andersen
Jacobson became a major supplier.
 |
After the Carterphone decision customers were allowed to non-telephone Company equipment directly to telephone lines. Commercial modems of 300 and 600 baud duplex capability became available, but were frustratingly slow for display users. Students at the Stanford AI lab developed and built a number of asymmetric modems: 1200 baud from computer to terminal and 150 baud from keyboard to the SAIL computer. The design was copied in other academic sites, but was obsoleted when 1200 baud full-duplex modems became available at less than $1000 in 1976.
The direct-Coupled Asymmetric Data Modem
shown has 150 send / 1200 baud receive capability. It was designed by
Kok Chen of the Radar astronomy group of Prof. Allen M. Peterson in
1974. Kok Chen was also active among the LOTS group (Ralph Gorin, Len Bosack (later a
founder of CISCO), et al.).
When most CS AI graduate students lost their office space during the
move from the D.C. Powers Lab
(in the background) to
Margaret Jacks Hall on Campus, Kok Chen released his homemade 1200/150
modem design to the guys at the CS department so that the displaced
students could at least view data at 1200 baud instead of 300. A couple of
hundred boards may have been built.
floor3 right front and rear
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |